LeetCode第47题: 全排列II
题目描述:
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2]
输出:
[[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]]
题目链接:
47. 全排列 II - 力扣(Leetcode)
解题思路:
这道题跟46题类似,用深度优先遍历,暴力搜索nums数组,然后回溯时恢复标记数组的原状。
对于递归函数,其函数出口应当为:在判断递归深度等于nums数组的长度时,将path序列添加到结果集中并返回。
我们可以画出树形结构来帮助理解:
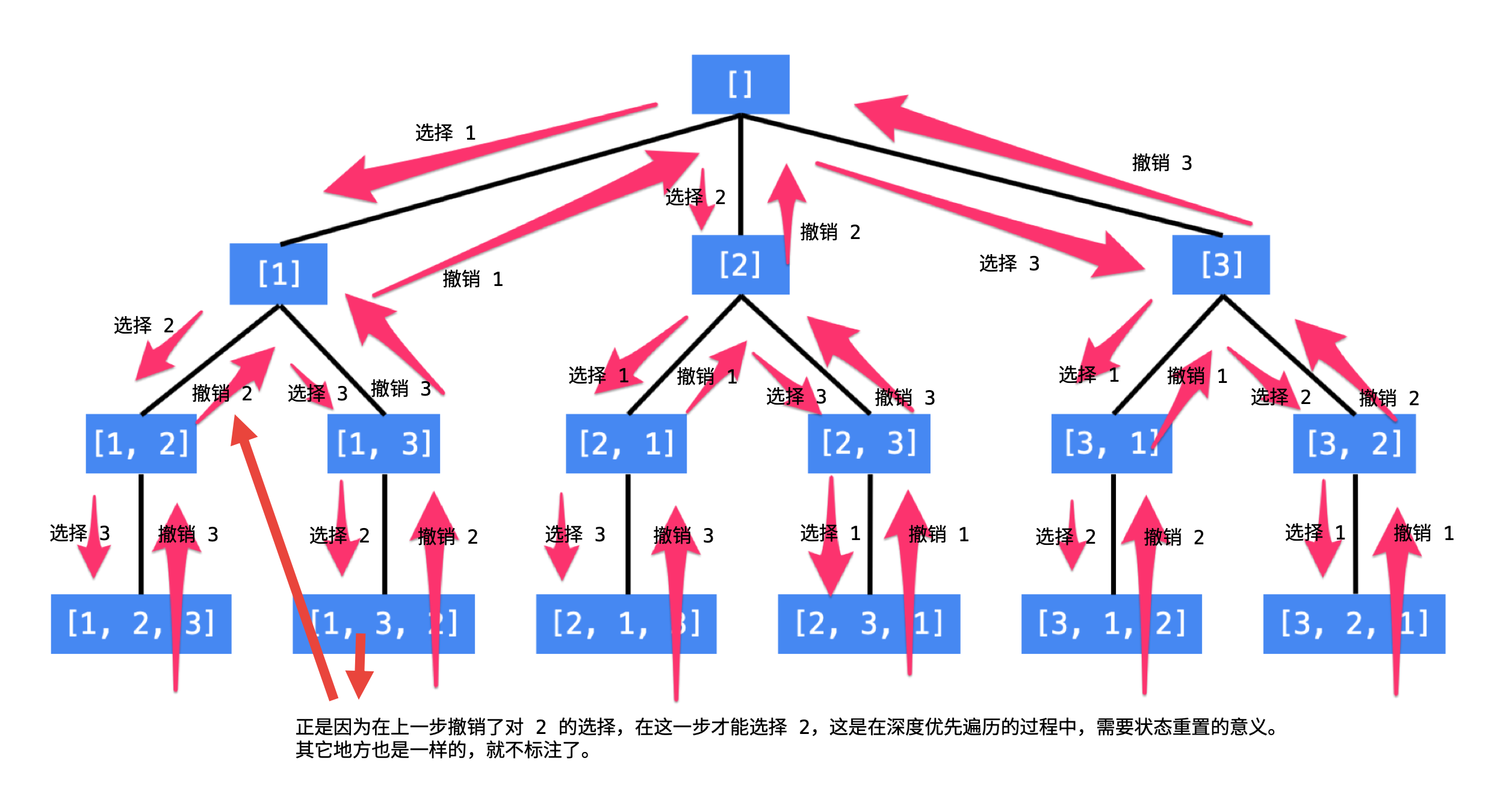
1
2
3
4
| if(depth==len){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
|
函数体中,遍历nums数组的每一个元素,对其进行标记后,将其添加至path序列中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){
if(!used[i]){
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i]=true;
dfs(len,nums,depth+1,path,used);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
|
不过这道题要求去除重复的序列,我首先想到的就是利用HashSet去重:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| class Solution {
static List<List<Integer>> result;
static HashSet<List<Integer>>set;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
set = new HashSet<>();
result = new ArrayList<>();
int len = nums.length;
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean used[] = new boolean[nums.length];
if(nums.length==0){
return result;
}
dfs(len,nums,0,path,used);
for(List list:set){
result.add(list);
}
return result;
}
static void dfs(int len,int []nums,int depth,List<Integer> path,boolean []used){
if(depth==len){
if(!set.contains(path))
set.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){
if(!used[i]){
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i]=true;
dfs(len,nums,depth+1,path,used);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
|
我们可以看到,这种写法的耗时还是比较高。原因是在递归过程中时需要进行剪枝。
思路是:在遍历的过程中,一边遍历一遍检测,在一定会产生重复结果集的地方剪枝。
如果要比较两个列表是否一样,一个容易想到的办法是对列表分别排序,然后逐个比对。既然要排序,我们就可以 在搜索之前就对候选数组排序,一旦发现某个分支搜索下去可能搜索到重复的元素就停止搜索,这样结果集中不会包含重复列表。
画出树形结构如下:重点想象深度优先遍历在这棵树上执行的过程,哪些地方遍历下去一定会产生重复,这些地方的状态的特点是什么? 对比图中标注 ① 和 ② 的地方。相同点是:这一次搜索的起点和上一次搜索的起点一样。不同点是:
- 标注 ① 的地方上一次搜索的相同的数刚刚被撤销;
- 标注 ② 的地方上一次搜索的相同的数刚刚被使用。
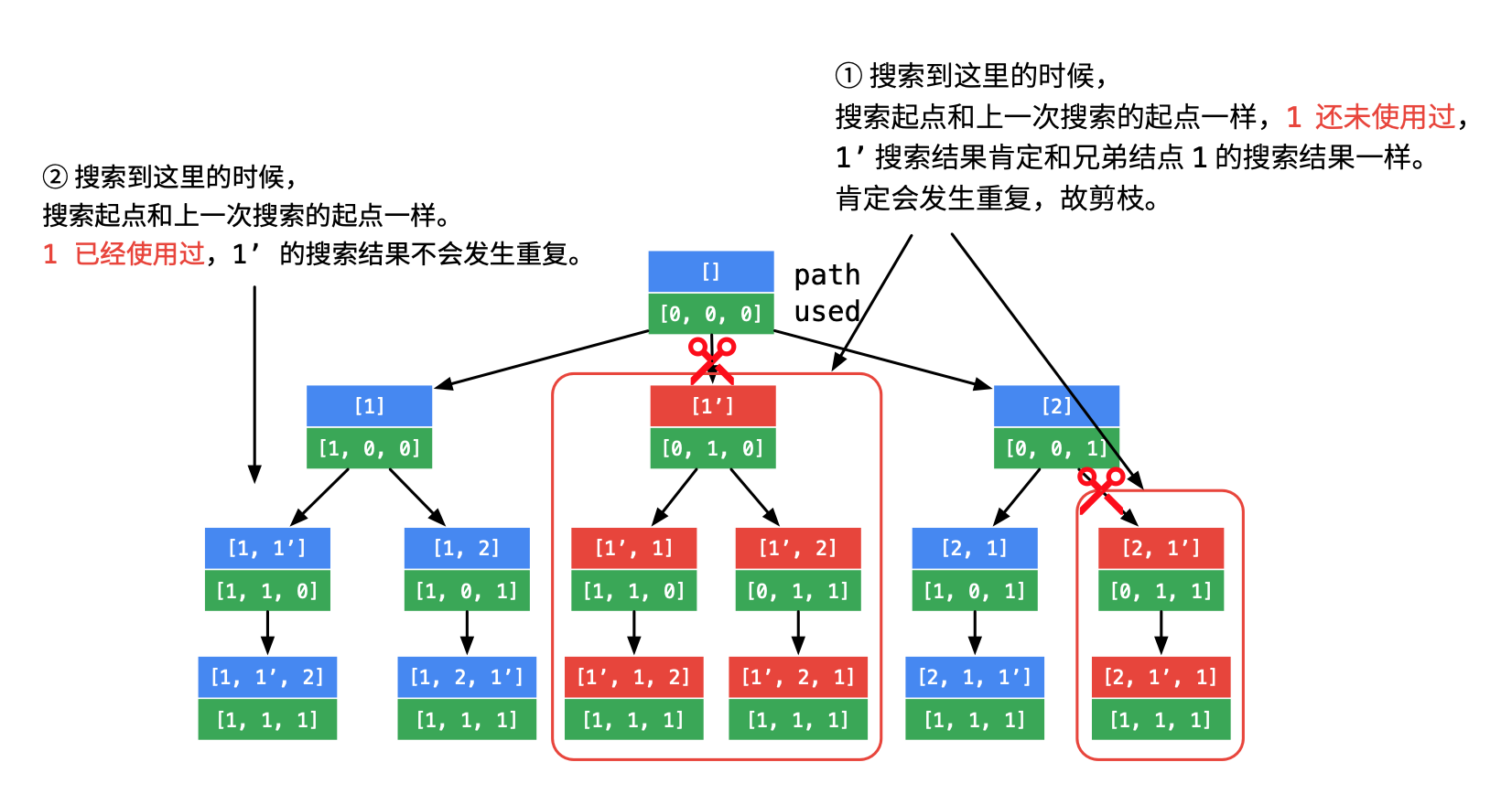
产生重复结点的地方,正是图中标注了「剪刀」,且被绿色框框住的地方。
大家也可以把第 2 个 1 加上 ‘ ,即 [1, 1’, 2] 去想象这个搜索的过程。只要遇到起点一样,就有可能产生重复。这里还有一个很细节的地方:
- 在图中 ② 处,搜索的数也和上一次一样,但是上一次的 1 还在使用中;
- 在图中 ① 处,搜索的数也和上一次一样,但是上一次的 1 刚刚被撤销,正是因为刚被撤销,下面的搜索中还会使用到,因此会产生重复,剪掉的就应该是这样的分支。
代码实现方面,在第 46 题的基础上,要加上这样一段代码:
1
2
3
| if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
|
整体实现代码(java):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| class Solution {
static List<List<Integer>> result;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
int len = nums.length;
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean used[] = new boolean[nums.length];
if(nums.length==0){
return result;
}
dfs(len,nums,0,path,used);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int len,int []nums,int depth,List<Integer> path,boolean []used){
if(depth==len){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){
if(used[i])continue;
if(i>0&&!used[i-1]&&nums[i-1]==nums[i]){
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i]=true;
dfs(len,nums,depth+1,path,used);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
|